The first steps of a bitcoin wallet
I started studying decentralized finance for a potential project opportunity. Here is what I learnt while creating my first bitcoin wallet.
⚠️ Do additional research if you plan to store a significant amount of bitcoins in your wallet. In my examples I am ignoring several recommended precautions.
⚠️ If you are interested in bitcoins as an investment, don’t. The only judicious investment for small savers are exchange-traded funds (ETFs), research those instead.
⚠️ As a rule of thumb: if someone requested you a bitcoin-related payment, it is a scam. Be careful and check bitcoin’s page about scams before regretting it.
Getting on the bitcoin network
In traditional finance you have a bank account. You connect to the bank’s server to see your balance and order transactions. The bank performs the operations on your behalf.
Bitcoins don’t rely on any bank’s servers. There is a peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers (nodes) talking to each other. The nodes share the blockchain: a record of every transaction in bitcoin’s history. New transactions are communicated over the P2P network and stored in new blocks of the blockchain.
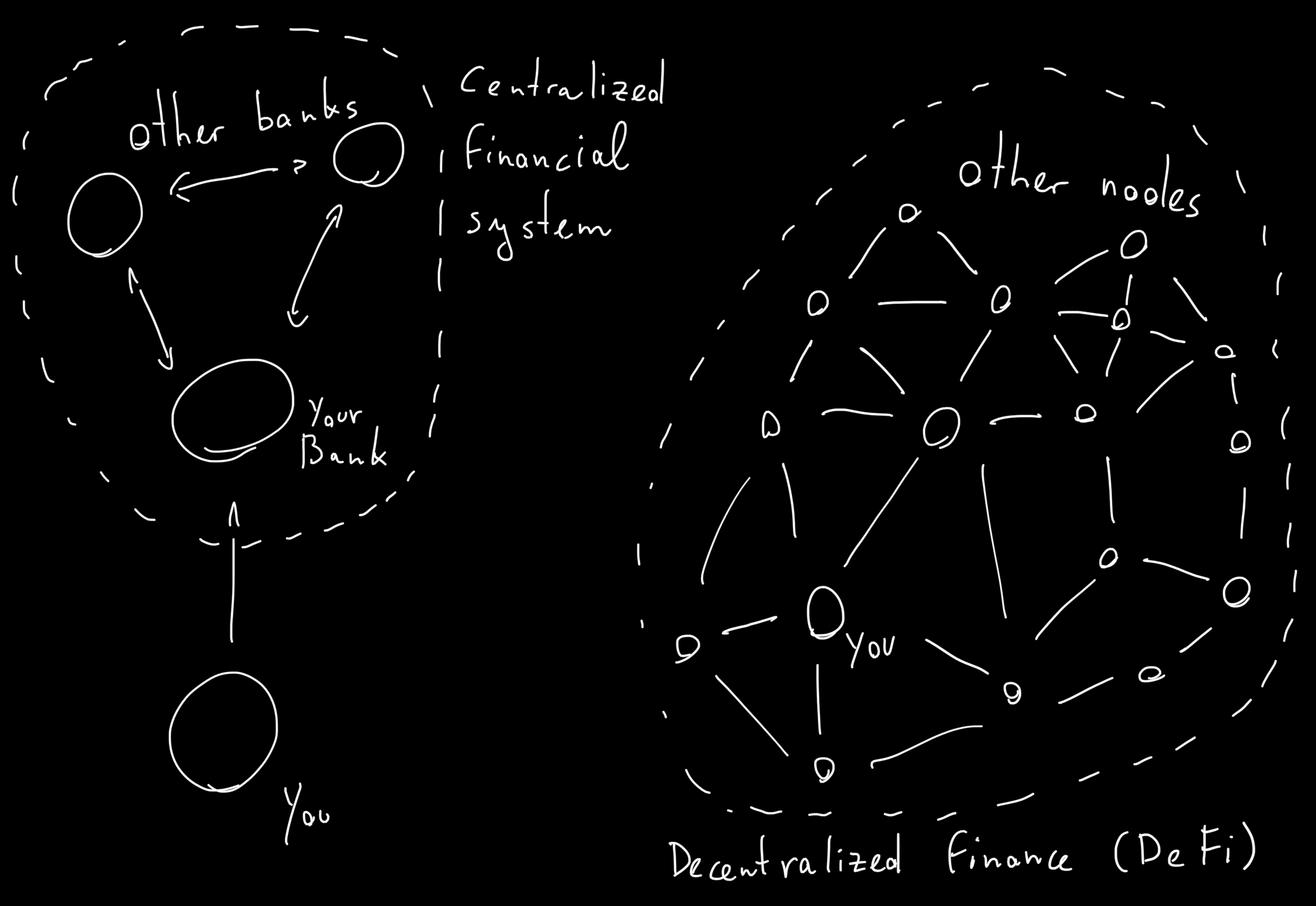
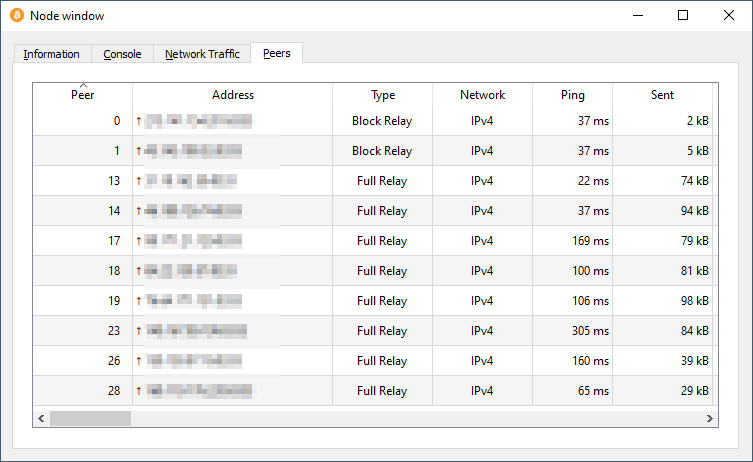
You can connect to the bitcoin network with Bitcoin Core1. Bitcoin Core connects to some nodes of the bitcoin P2P network. By running it, your machine also becomes one of the nodes. You can see the nodes you are connected to on the node window.
⚠️ Connecting to the bitcoin network exposes your IP address. If you care about anonymity, you should take additional precautions2.
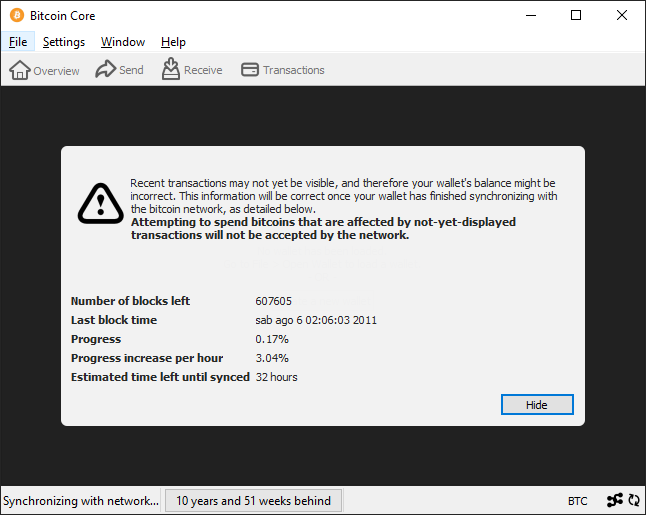
The first time you open Bitcoin Core, it downloads a full copy of the blockchain.3 Once the download is complete, your copy of the blockchain is also shared. Your machine and the other nodes keep each other’s copy of the blockchain up to date.
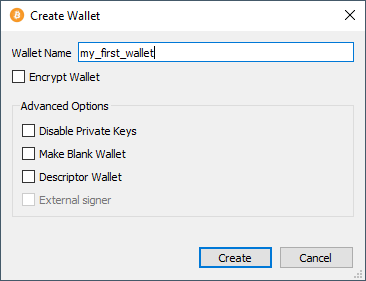
Creating the wallet
Bitcoins are stored in wallets. Wallets consists of a private key and a public key. The public key identifies your wallet on the network and is necessary to receive funds. The private key is necessary to sign transactions from your wallet to other wallets. Bitcoin Core can create wallets and store the keys on your machine4 5. The keys of the wallet are stored in a wallet.dat file, which should be backed up.
⚠️ If you lose your private key, you won’t be able to transfer funds from your wallet. If your private key is leaked, your wallet will be emptied. Unlike traditional finance, bitcoins don’t allow to reverse transactions. Losing exclusive access to your bitcoin wallet is irreversible.
The new wallet does not exists on the blockchain yet, only as the locally saved keys. Once there is at least one transaction to your wallet, it will be visible to the bitcoin network.
Receiving the first bitcoins on the wallet
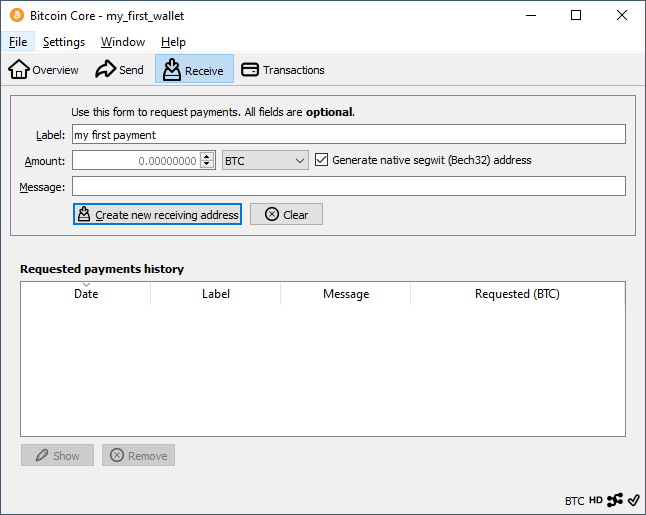
You don’t need to share your public key to receive bitcoins on your wallet. It is more common to provide an address. There can be multiple addresses for the same wallet. It is recommended to create a separate address for every single transaction6.
⚠️ You should backup your wallet after every address creation. Without the backup, you may lose incoming payments to the address.
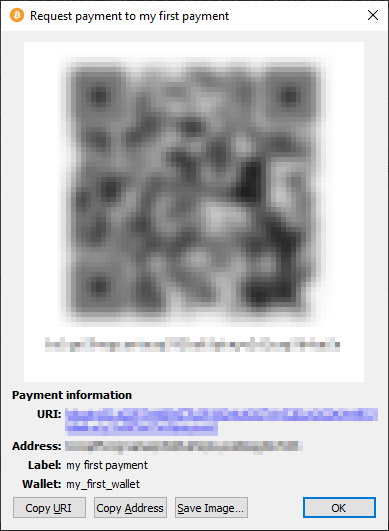
Bitcoin Core can create addresses for your wallet. You can copy the address directly or share it as an URI or QR code for other applications.
You can buy bitcoins for traditional currencies. There are several exchanges to buy bitcoins, I used MoonPay, which is the one on the main bitcoin website7. At one step you must enter the address.
After entering the payment information, you need to wait for the transaction to be processed. MoonPay takes care of getting the bitcoins from a wallet and transferring them to your wallet. After MoonPay signs the transaction with its private key, the next steps take place in the bitcoin network.
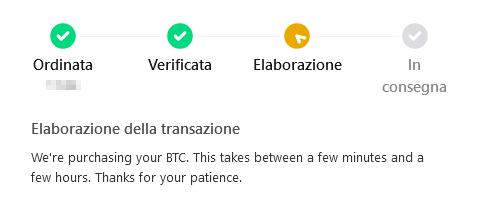
The transaction is communicated to the nodes and the miners can see it. The miners will put the bitcoin in a block with other transactions and try adding it to the blockchain. The first successful miner will receive a reward from your bitcoins8. This is referred to as bitcoin mining.
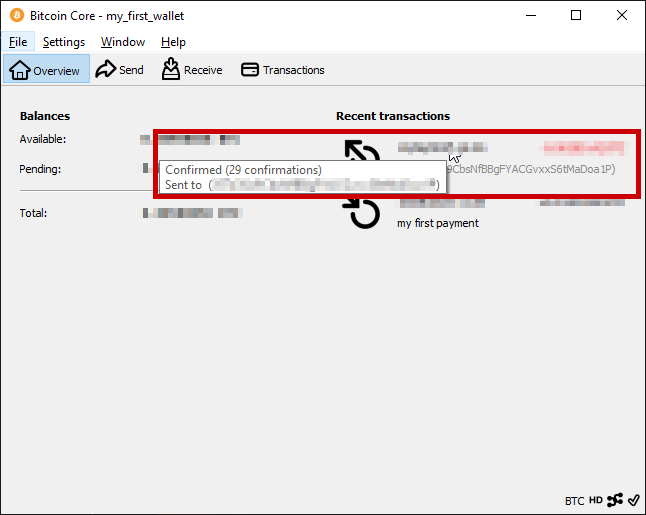
The new block of the blockchain is downloaded by Bitcoin Core, which recognizes the transaction and shows it in your wallet. Now the wallet exists on the blockchain and not just as locally saved keys.
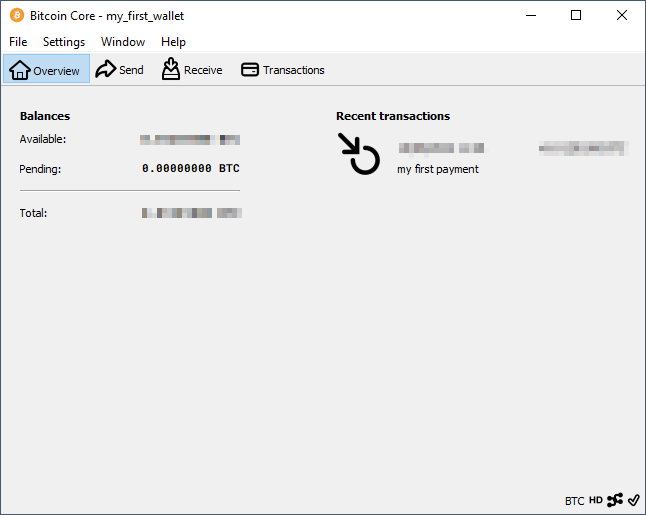
Sending bitcoins to another wallet
Now that we have bitcoins, it is time to use them. As you can receive payments to an address, other recipients can provide an address to get bitcoins from you. E.g. there is an address to support the war effort in Ukraine.

Bitcoin Core also allows sending bitcoins from your wallet to another. You just need to copy the recipient’s address and select the amount. By selecting a longer confirmation time target, it is possible to pay a lower transaction fee. The fee is paid just to the miners within the bitcoin network.
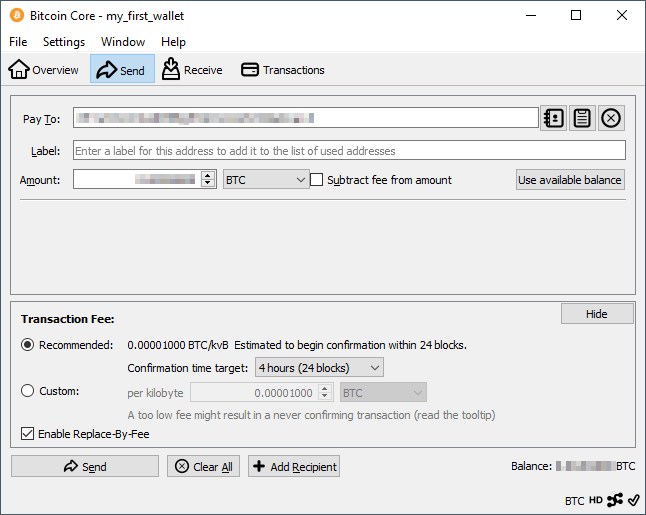
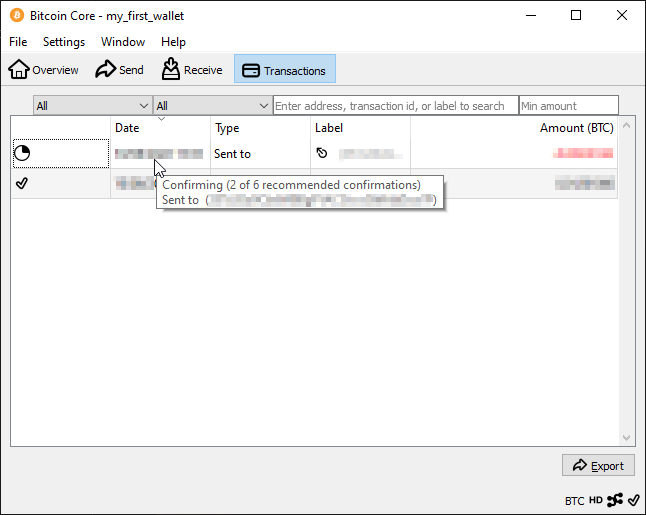
After signing, Bitcoin Core shares the transaction to the network. Miners will include the transaction to a block and try adding it to the blockchain. As long as the transaction is not in the blockchain, it is marked as unconfirmed.
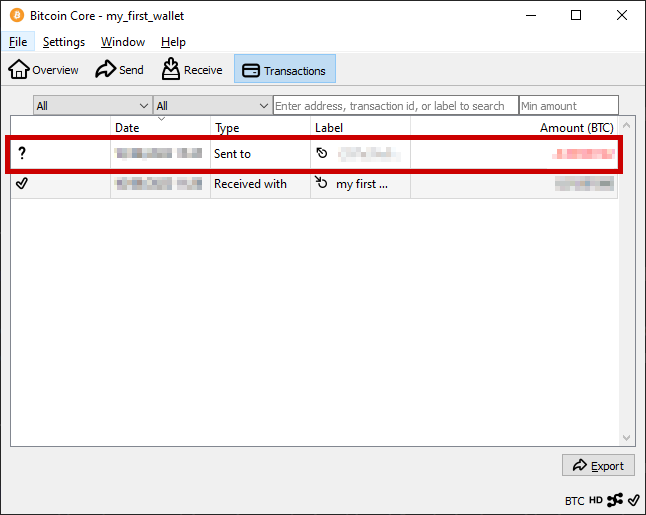
Bitcoin Core waits for multiple confirmations to ensure that the transaction is on the longest blockchain. Once the transaction has been added to the blockchain, it is shown as successful.
Links
Footnotes
-
“[Bitcoin Core] is a direct descendant of the original Bitcoin software client released by Satoshi Nakamoto after he published the famous Bitcoin whitepaper.” About Bitcoin Core ↩
-
Bitcoin Core supports the The Onion Router (Tor). It can help protect your anonymity, but is not 100% safe. ↩
-
At the time of writing the blockchain is about 400 GB big. ↩
-
This is called a software wallet. You can use a hardware wallet or an offline wallet instead. Each kind of wallet is not perfect and has different pros and cons. ↩
-
There are services which save the keys on your behalf and provide a risk trade-off. You basically exchange the risk of you screwing up with the risk of the service provider screwing up. ↩
-
There are privacy and security reasons for which is preferable to do so. ↩
-
There are usually fees on marketplaces in addition to the network fees in bitcoin. ↩
-
There can be multiple miners adding a block at the same time or malicious agents trying to replace transactions at earlier stages. The bitcoin network is designed to be eventually consistent, as only the longest blockchain is considered. ↩